
Unlike fiat money, which can be unrestrictedly printed by central banks, Bitcoin is often marketed as an inflation hedge since its total supply is limited to 21 million coins only. Such a cap makes bitcoin less prone to inflation.

Due to the recent events we observe that the value of fiat money take a tumble, while the value of limited-supply assets like stocks, real estate – not to mention BTC – they all skyrocket. Seeing bitcoin as a panacea for inflation attracted a great number of traditional investors, which contributed to its considerable growth.
What exactly is inflation?
Inflation takes place when currencies lose value over time and when there’s a hike in purchasing power. Owing to their limited supply, crypto like Bitcoin generally experience low inflation rates. As opposed to traditional currencies, the issuance of which is controlled by central banks, cryptocurrencies are less exposed to external factors, making them less susceptible to price escalation.

Inflation strikes a wide spectrum of products and services, including utilities, automobiles, food, medical care, and housing. The prevalence of such phenomenon in an economy affects both individual consumers and businesses. To put it otherwise, it reduces a consumer’s spending power, makes savings less valuable and delays retirement. Central banks around the world keep track of inflation by setting some sort of target level. Should the inflation rate surpass this figure, banks resort to proper measures to flatline the situation.
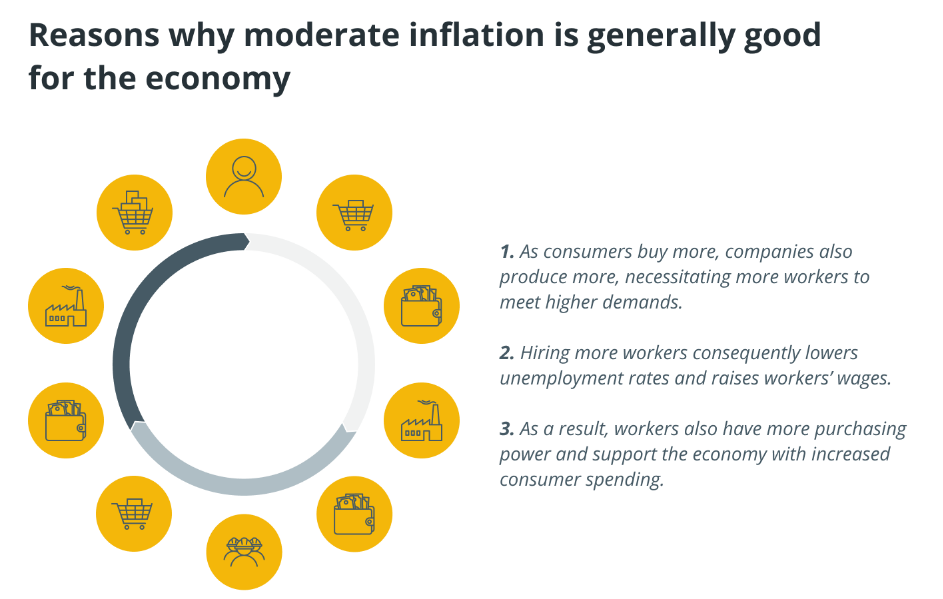
Is inflation good or bad for an economy?
Inflation cutting the purchasing power of any given currency is not always viewed as a bad thing. Most economists believe that moderate levels of inflation can benefit an economy.
A moderate inflation rate drives consumer spending. This is crucial for any economy to flourish.
In a healthy economy, stable inflation rates are to be expected, indicating increased spending on goods and services by consumers and businesses. As demand surpasses supply, producers raise prices, thus fueling inflation. In this context, inflation can be considered a positive development.
However, any sudden rise or fall in prices is generally not a welcome sign. Hyperinflation, or rampant price increases, causes consumers to anticipate even steeper upswings, which can stimulate demand even more. This in turn leads to further price hikes and aggravates inflation.
Deflation, on the other hand, features a steady price drop, adversely affecting an economy. When this happens, consumers hold off their purchases while awaiting of lower prices down the road. Producers also keep lowering prices to attract buyers.
What inflation means for BTC?
While the economics around the Bitcoin market is intricate, some cryptocurrencies are designed in such a way as to combat inflation or experience predictable and moderate inflation rates. While it is often claimed that Bitcoin is a bailout from inflation, recent economic developments have seen Bitcoin performing less as a pure hedge.
What part does Bitcoin play in inflation?
Largely driven by institutional investments, the cryptocurrency in question has become increasingly aligned with general market movements. This implies that when the market collapses, Bitcoin likely crumbles as well.
So as soon as the news of inflation strikes and the Fed emerge, they will likely enact a dual mandate. Interest rates are to soar, and there will be monetary poilcy tightening. As a result, assets (including crypto like Bitcoin) will see a price decline.
Does crypto space even experience any inflation?
Absolutely. Cryptocurrencies suffer inflation — even the first-ever crypto, which is often seen as “inflation-resistant.” Much like gold, Bitcoin experiences inflation as more of it is mined. Nonetheless, given that mining for new BTCs is automatically reduced by 50% every four years (the halving occurs), inflation rates are also bound to slide eventually.

Nowadays as Bitcoin’s value keeps rising against fiat currencies, its typical annual inflation rates aren’t usually a major area of concern for investors. Other cryptocurrencies, however, may perform differently.
Stablecoins, for instance, are pegged to fiat money and can be considered a low-volatility crypto for saving money. What’s more, stablecoins are subject to inflation so they could lose value over time. As their reserved currency loses value, so do the stablecoins.
Conclusion
Bitcoin is unlikely to dethrone major centralized currencies, but it has altered the financial landscape since its inception in 2009. Its one-of-a-kind technology has revolutionized DeFi sector and is beneficial to unbanked clients in far-reaching and low-income territories.
Blockchain technology has paved the way for numerous innovations, but its primary function is to provide users with a secure, permissionless and decentralized way to conduct financial transactions. Bitcoin, alongside other crypto assets, serves as inflation and recession-resistant alternatives to fiat.
